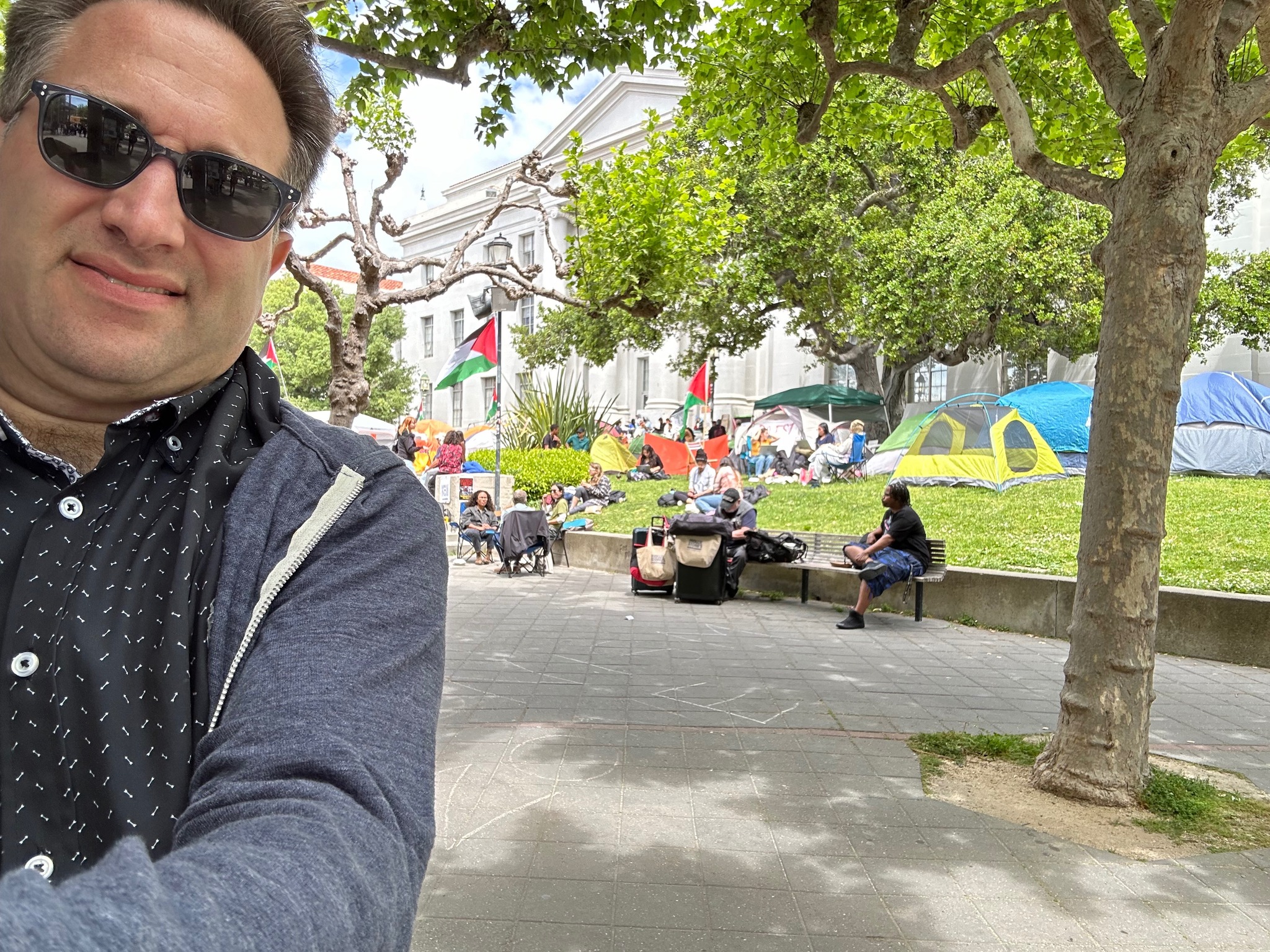
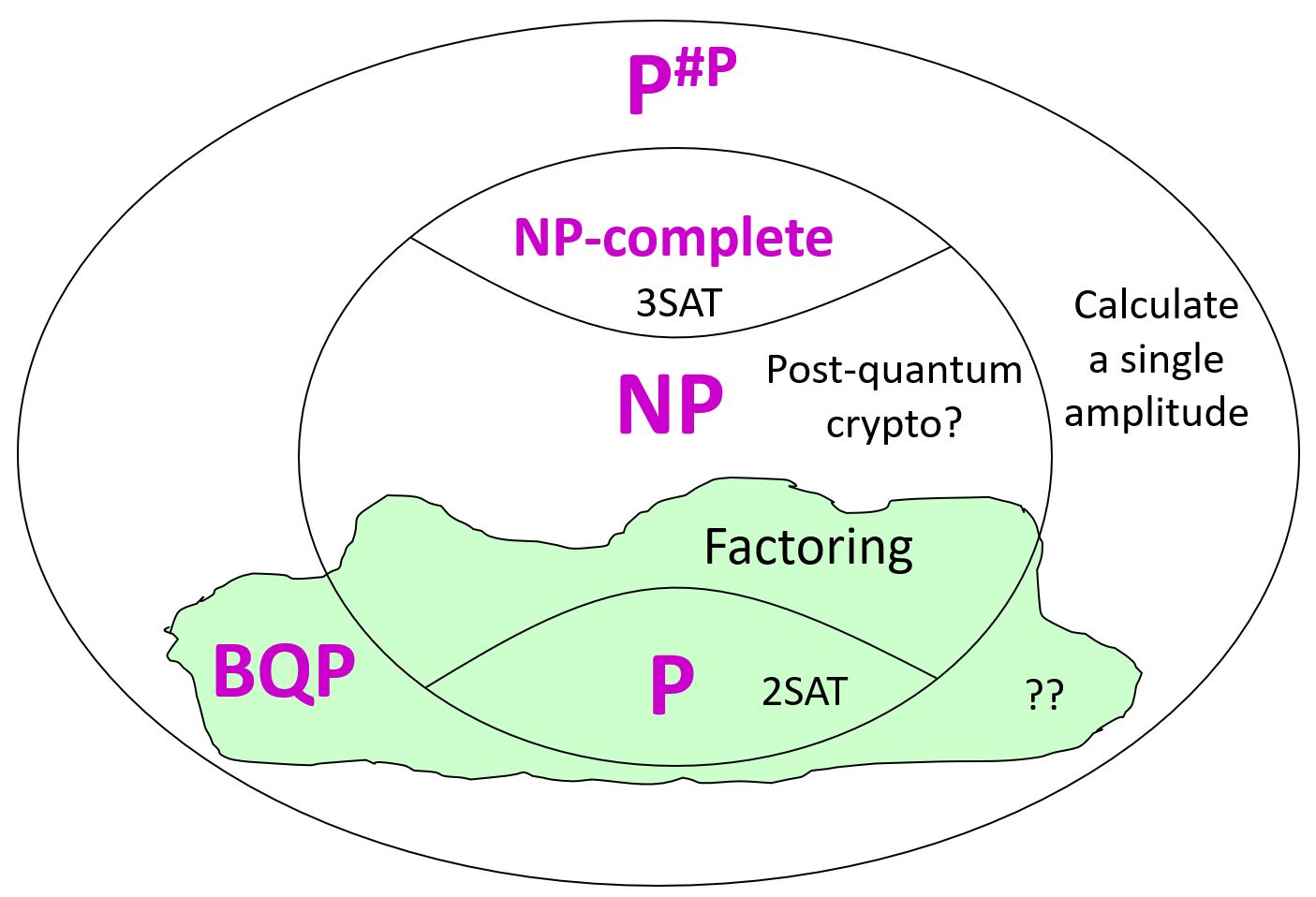
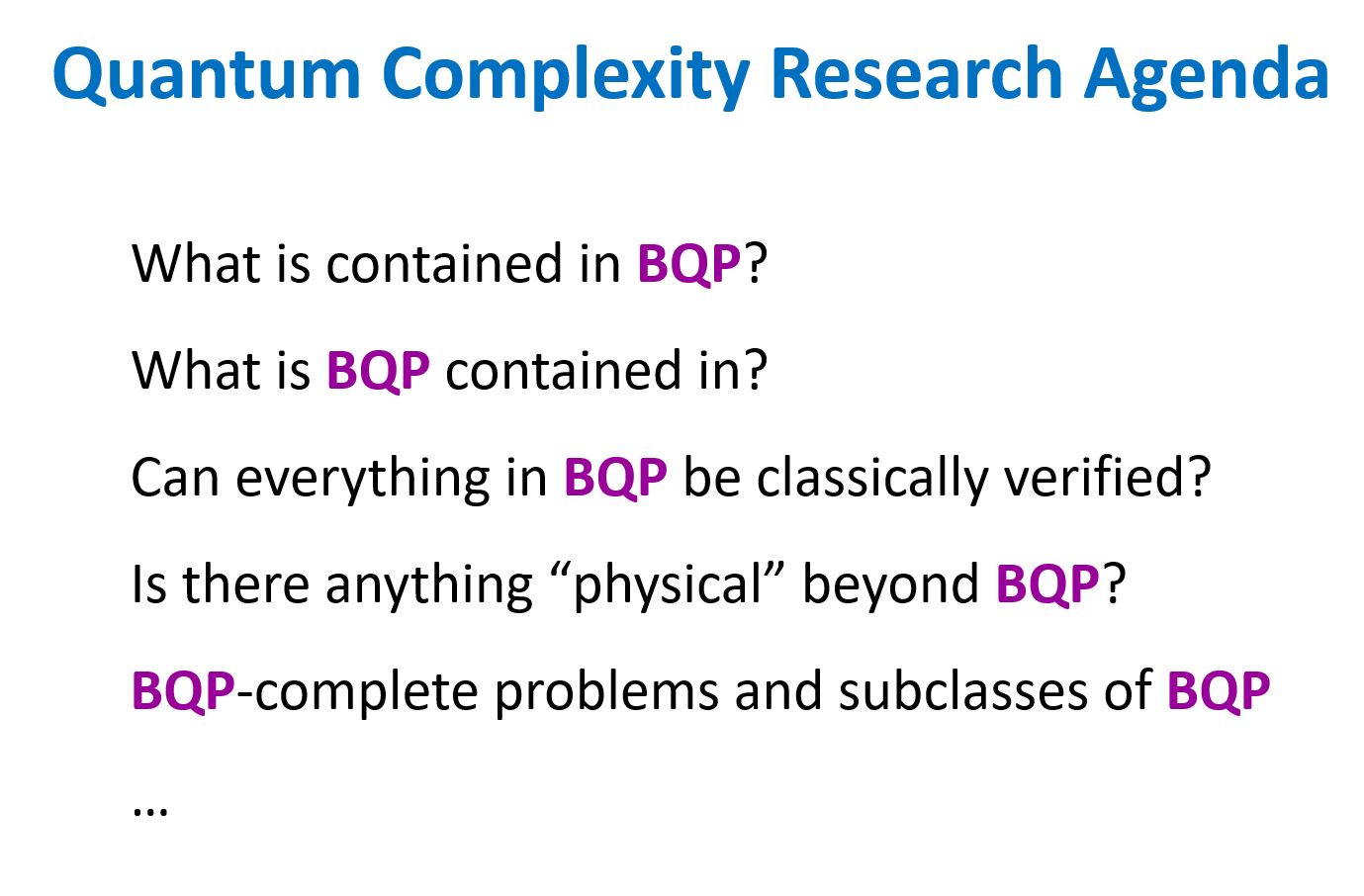
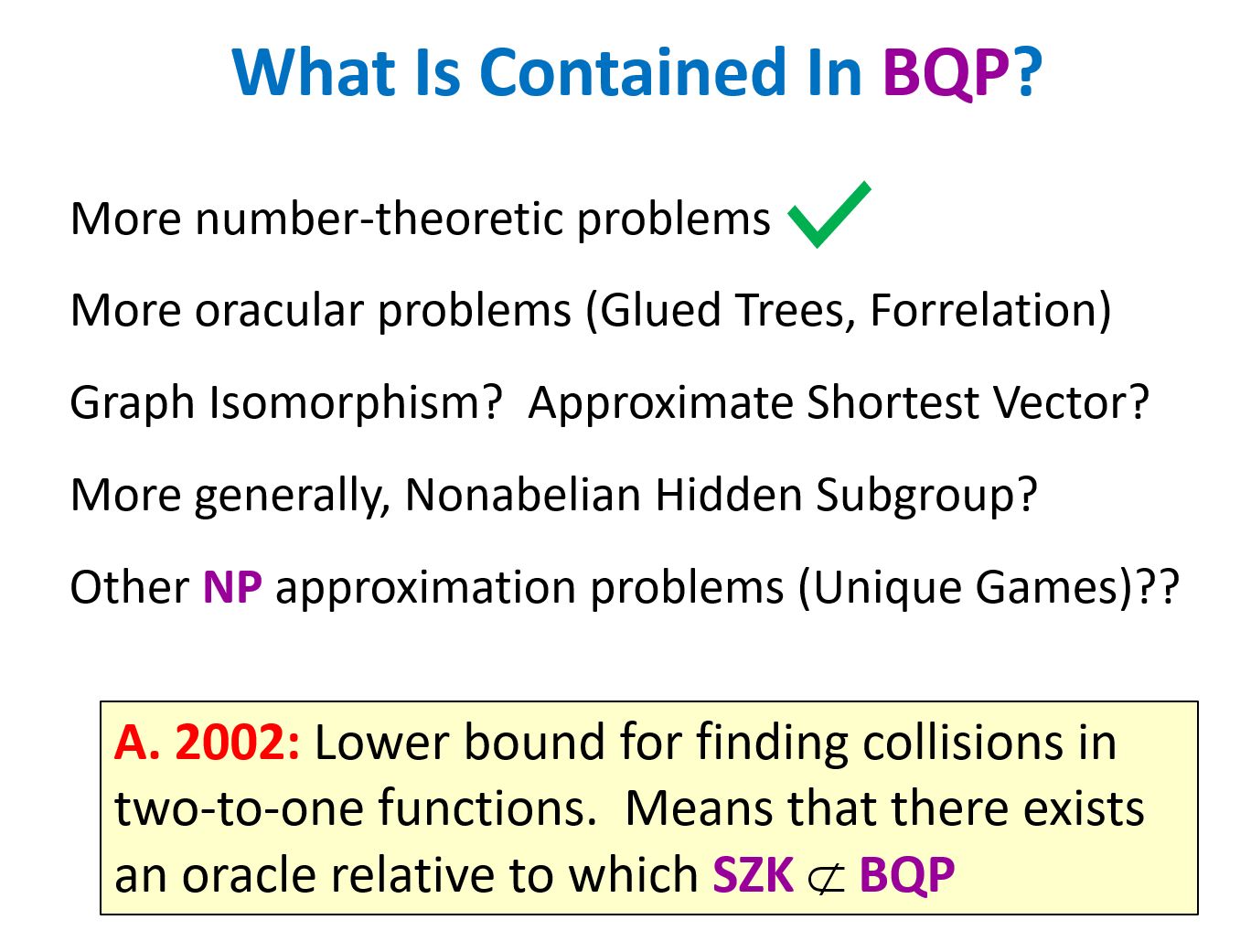
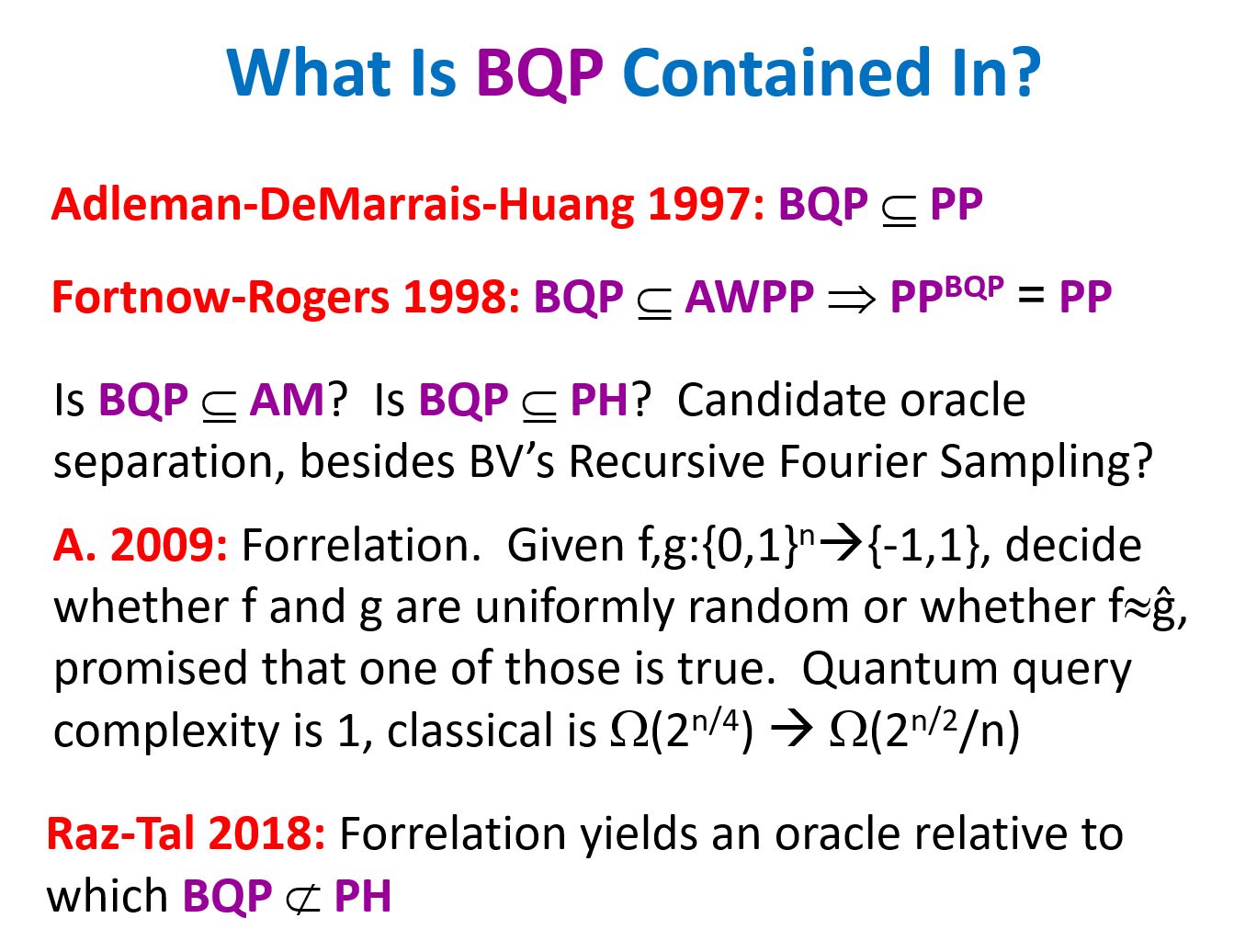
A week ago I attended LessOnline, a rationalist blogging conference featuring many people I’ve known for years—Scott Alexander, Eliezer Yudkowsky, Zvi Mowshowitz, Sarah Constantin, Carl Feynman—as well as people I’ve known only online and was delighted to meet in person, like Joe Carlsmith and Jacob Falkovich and Daniel Reeves. The conference was at Lighthaven, a bewildering maze of passageways, meeting-rooms, sleeping quarters, gardens, and vines off Telegraph Avenue in Berkeley, which has recently emerged as the nerd Shangri-La, or Galt’s Gulch, or Shire, or whatever. I did two events at this year’s LessOnline: a conversation with Nate Soares about the Orthogonality Thesis, and an ask-me-anything session about quantum computing and theoretical computer science (no new ground there for regular consumers of my content).
What I’ll remember most from LessOnline is not the sessions, mine or others’, but the unending conversation among hundreds of people all over the grounds, which took place in parallel with the sessions and before and after them, from morning till night (and through the night, apparently, though I’ve gotten too old for that). It felt like a single conversational archipelago, the largest in which I’ve ever taken part, and the conference’s real point. (Attendees were exhorted, in the opening session, to skip as many sessions as possible in favor of intense small-group conversations—not only because it was better but also because the session rooms were too small.)
Within the conversational blob, just making my way from one building to another could take hours. My mean free path was approximately five feet, before someone would notice my nametag and stop me with a question. Here was my favorite opener:
“You’re Scott Aaronson?! The quantum physicist who’s always getting into arguments on the Internet, and who’s essentially always right, but who sustains an unreasonable amount of psychic damage in the process?”
“Yes,” I replied, not bothering to correct the “physicist” part.
One night, I walked up to Scott Alexander, who sitting on the ground, with his large bald head and a blanket he was using as a robe, resembled a monk. “Are you enjoying yourself?” he asked.
I replied, “you know, after all these years of being coy about it, I think I’m finally ready to become a Rationalist. Is there, like, an initiation ritual or something?”
Scott said, “Oh, you were already initiated a decade ago; you just didn’t realize it at the time.” Then he corrected himself: “two decades ago.”
The first thing I did, after coming out as a Rationalist, was to get into a heated argument with Other Scott A., Joe Carlsmith, and other fellow-Rationalists about the ideas I set out twelve years ago in my Ghost in the Quantum Turing Machine essay. Briefly, my argument was that the irreversibility and ephemerality of biological life, which contrasts with the copyability, rewindability, etc. of programs running on digital computers, and which can ultimately be traced back to microscopic details of the universe’s initial state, subject to the No-Cloning Theorem of quantum mechanics, which then get chaotically amplified during brain activity … might be a clue to a deeper layer of the world, one that we understand about as well as the ancient Greeks understood Newtonian physics, but which is the layer where mysteries like free will and consciousness will ultimately need to be addressed.
I got into this argument partly because it came up, but partly also because this seemed like the biggest conflict between my beliefs and the consensus of my fellow Rationalists. Maybe part of me wanted to demonstrate that my intellectual independence remained intact—sort of like a newspaper that gets bought out by a tycoon, and then immediately runs an investigation into the tycoon’s corruption, as well as his diaper fetish, just to prove it can.
The funny thing, though, is that all my beliefs are the same as they were before. I’m still a computer scientist, an academic, a straight-ticket Democratic voter, a liberal Zionist, a Jew, etc. (all identities, incidentally, well-enough represented at LessOnline that I don’t even think I was the unique attendee in the intersection of them all).
Given how much I resonate with what the Rationalists are trying to do, why did it take me so long to identify as one?
Firstly, while 15 years ago I shared the Rationalists’ interests, sensibility, and outlook, and their stances on most issues, I also found them bizarrely, inexplicably obsessed with the question of whether AI would soon become superhumanly powerful and change the basic conditions of life on earth, and with how to make the AI transition go well. Why that, as opposed to all the other sci-fi scenarios one could worry about, not to mention all the nearer-term risks to humanity?
Suffice it to say that empirical developments have since caused me to withdraw my objection. Sometimes weird people are weird merely because they see the future sooner than others. Indeed, it seems to me that the biggest thing the Rationalists got wrong about AI was to underestimate how soon the revolution would happen, and to overestimate how many new ideas would be needed for it (mostly, as we now know, it just took lots more compute and training data). Now that I, too, spend some of my time working on AI alignment, I was able to use LessOnline in part for research meetings with colleagues.
A second reason I didn’t identify with the Rationalists was cultural: they were, and are, centrally a bunch of twentysomethings who “work” at an ever-changing list of Berkeley- and San-Francisco-based “orgs” of their own invention, and who live in group houses where they explore their exotic sexualities, gender identities, and fetishes, sometimes with the aid of psychedelics. I, by contrast, am a straight, monogamous, middle-aged tenured professor, married to another such professor and raising two kids who go to normal schools. Hanging out with the Rationalists always makes me feel older and younger at the same time.
So what changed? For one thing, with the march of time, a significant fraction of Rationalists now have marriages, children, or both—indeed, a highlight of LessOnline was the many adorable toddlers running around the Lighthaven campus. Rationalists are successfully reproducing! Some because of explicit pronatalist ideology, or because they were persuaded by Bryan Caplan’s arguments in Selfish Reasons to Have More Kids. But others simply because of the same impulses that led their ancestors to do the same for eons. And perhaps because, like the Mormons or Amish or Orthodox Jews, but unlike typical secular urbanites, the Rationalists believe in something. For all their fears around AI, they don’t act doomy, but buzz with ideas about how to build a better world for the next generation.
At a LessOnline parenting session, hosted by Julia Wise, I was surrounded by parents who worry about the same things I do: how do we raise our kids to be independent and agentic yet socialized and reasonably well-behaved, technologically savvy yet not droolingly addicted to iPad games? What schooling options will let them accelerate in math, save them from the crushing monotony that we experienced? How much of our own lives should we sacrifice on the altar of our kids’ “enrichment,” versus trusting Judith Rich Harris that such efforts quickly hit a point of diminishing returns?
A third reason I didn’t identify with the Rationalists was, frankly, that they gave off some (not all) of the vibes of a cult, with Eliezer as guru. Eliezer writes in parables and koans. He teaches that the fate of life on earth hangs in the balance, that the select few who understand the stakes have the terrible burden of steering the future. Taking what Rationalists call the “outside view,” how good is the track record for this sort of thing?
OK, but what did I actually see at Lighthaven? I saw something that seemed to resemble a cult only insofar as the Beatniks, the Bloomsbury Group, the early Royal Society, or any other community that believed in something did. When Eliezer himself—the bearded, cap-wearing Moses who led the nerds from bondage to their Promised Land in Berkeley—showed up, he was argued with like anyone else. Eliezer has in any case largely passed his staff to a new generation: Nate Soares and Zvi Mowshowitz have found new and, in various ways, better ways of talking about AI risk; Scott Alexander has for the last decade written the blog that’s the community’s intellectual center; figures from Kelsey Piper to Jacob Falkovich to Aella have taken Rationalism in new directions, from mainstream political engagement to the … err … statistical analysis of orgies.
I’ll say this, though, on the naysayers’ side: it’s really hard to make dancing to AI-generated pop songs about Bayes’ theorem and Tarski’s definition of truth not feel cringe, as I can now attest from experience.
The cult thing brings me to the deepest reason I hesitated for so long to identify as a Rationalist: namely, I was scared that if I did, people whose approval I craved (including my academic colleagues, but also just randos on the Internet) would sneer at me. For years, I searched of some way of explaining this community’s appeal so reasonable that it would silence the sneers.
It took years of psychological struggle, and (frankly) solidifying my own place in the world, to follow the true path, which of course is not to give a shit what some haters think of my life choices. Consider: five years ago, it felt obvious to me that the entire Rationalist community might be about to implode, under existential threat from Cade Metz’s New York Times article, as well as RationalWiki and SneerClub and all the others laughing at the Rationalists and accusing them of every evil. Yet last week at LessOnline, I saw a community that’s never been thriving more, with a beautiful real-world campus, excellent writers on every topic who felt like this was the place to be, and even a crop of kids. How many of the sneerers are living such fulfilled lives? To judge from their own angry, depressed self-disclosures, probably not many.
But are the sneerers right that, even if the Rationalists are enjoying their own lives, they’re making other people’s lives miserable? Are they closet far-right monarchists, like Curtis Yarvin? I liked how The New Yorker put it in its recent, long and (to my mind) devastating profile of Yarvin:
The most generous engagement with Yarvin’s ideas has come from bloggers associated with the rationalist movement, which prides itself on weighing evidence for even seemingly far-fetched claims. Their formidable patience, however, has also worn thin. “He never addressed me as an equal, only as a brainwashed person,” Scott Aaronson, an eminent computer scientist, said of their conversations. “He seemed to think that if he just gave me one more reading assignment about happy slaves singing or one more monologue about F.D.R., I’d finally see the light.”
The closest to right-wing politics that I witnessed at LessOnline was a session, with Kelsey Piper and current and former congressional staffers, about the prospects for moderate Democrats to articulate a pro-abundance agenda that would resonate with the public and finally defeat MAGA.
But surely the Rationalists are incels, bitter that they can’t get laid? Again, the closest I saw was a session where Jacob Falkovich helped a standing-room-only crowd of mostly male nerds confront their fears around dating and understand women better, with Rationalist women eagerly volunteering to answer questions about their perspective. Gross, right? (Also, for those already in relationships, Eliezer’s primary consort and former couples therapist Gretta Duleba did a session on relationship conflict.)
So, yes, when it comes to the Rationalists, I’m going to believe my own lying eyes over the charges of the sneerers. The sneerers can even say about me, in their favorite formulation, that I’ve “gone mask off,” confirmed the horrible things they’ve always suspected. Yes, the mask is off—and beneath the mask is the same person I always was, who has an inordinate fondness for the Busy Beaver function and the complexity class BQP/qpoly, and who uses too many filler words and moves his hands too much, and who strongly supports the Enlightenment, and who once feared that his best shot at happiness in life would be to earn women’s pity rather than their contempt. Incorrectly, as I’m glad to report. From my nebbishy nadir to the present, a central thing that’s changed is that, from my family to my academic colleagues to the Rationalist community to my blog readers, I finally found some people who want what I have to sell.
Unrelated Announcements:
My replies to comments on this post might be light, as I’ll be accompanying my daughter on a school trip to the Galapagos Islands!
A few weeks ago, I was “ambushed” into leading a session on philosophy and theoretical computer science at UT Austin. (I.e., asked to show up for the session, but thought I’d just be a participant rather than the main event.) The session was then recorded and placed on YouTube—and surprisingly, given the circumstances, some people seemed to like it!
Friend-of-the-blog Alon Rosen has asked me to announce a call for nominations for a new theoretical computer science prize, in memory of my former professor (and fellow TCS blogger) Luca Trevisan, who was lost to the world too soon.
And one more: Mahdi Cheraghchi has asked me to announce the STOC’2025 online poster session, registration deadline June 12; see here for more. Incidentally, I’ll be at STOC in Prague to give a plenary on quantum algorithms; I look forward to meeting any readers who are there!
 Follow
Follow